按需选择你需要的频道内容
多个频道自由组合,创建专属于你的个性化空间。
 团队协作工具
团队协作工具
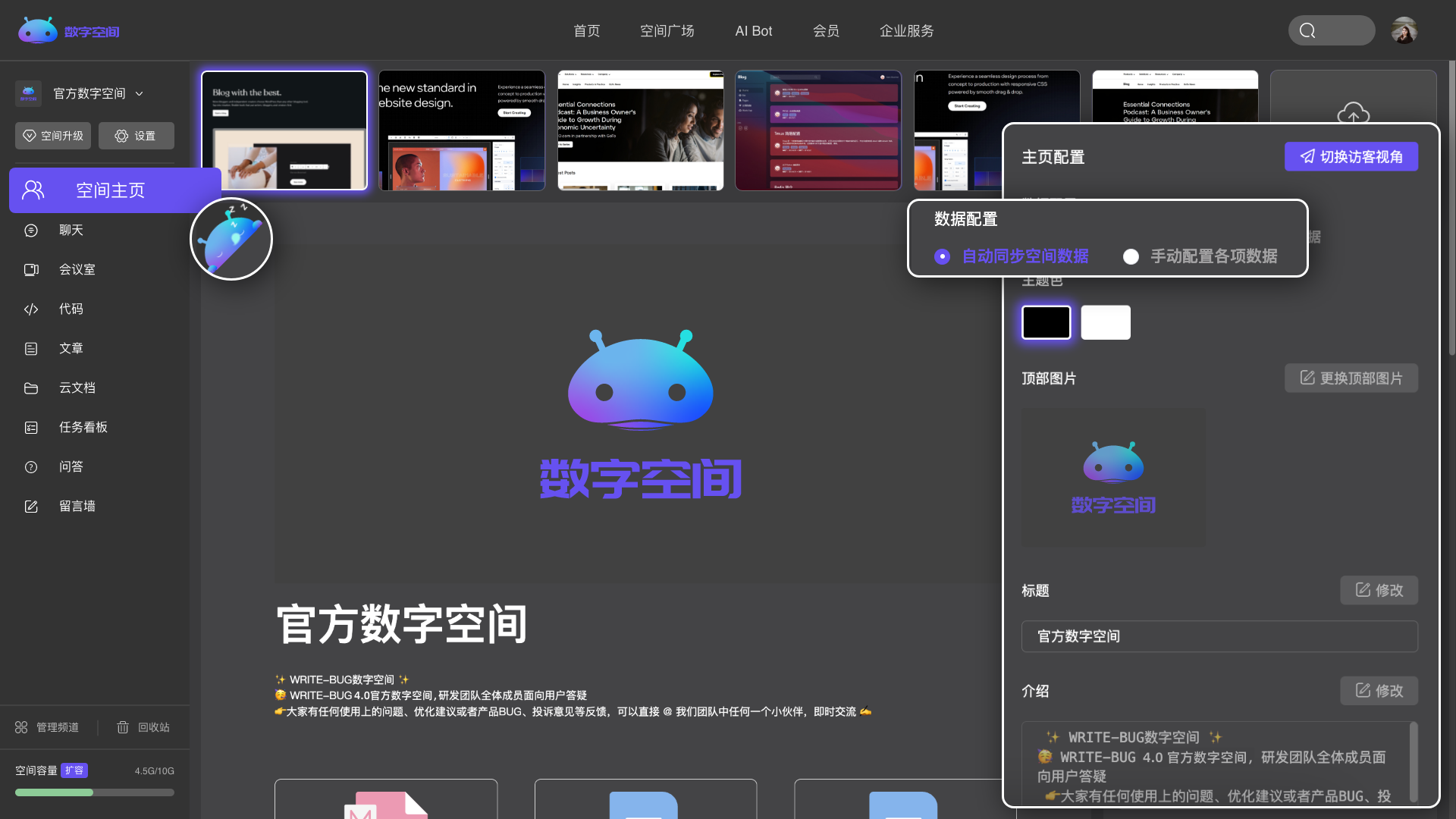
多个频道自由组合,创建专属于你的个性化空间。
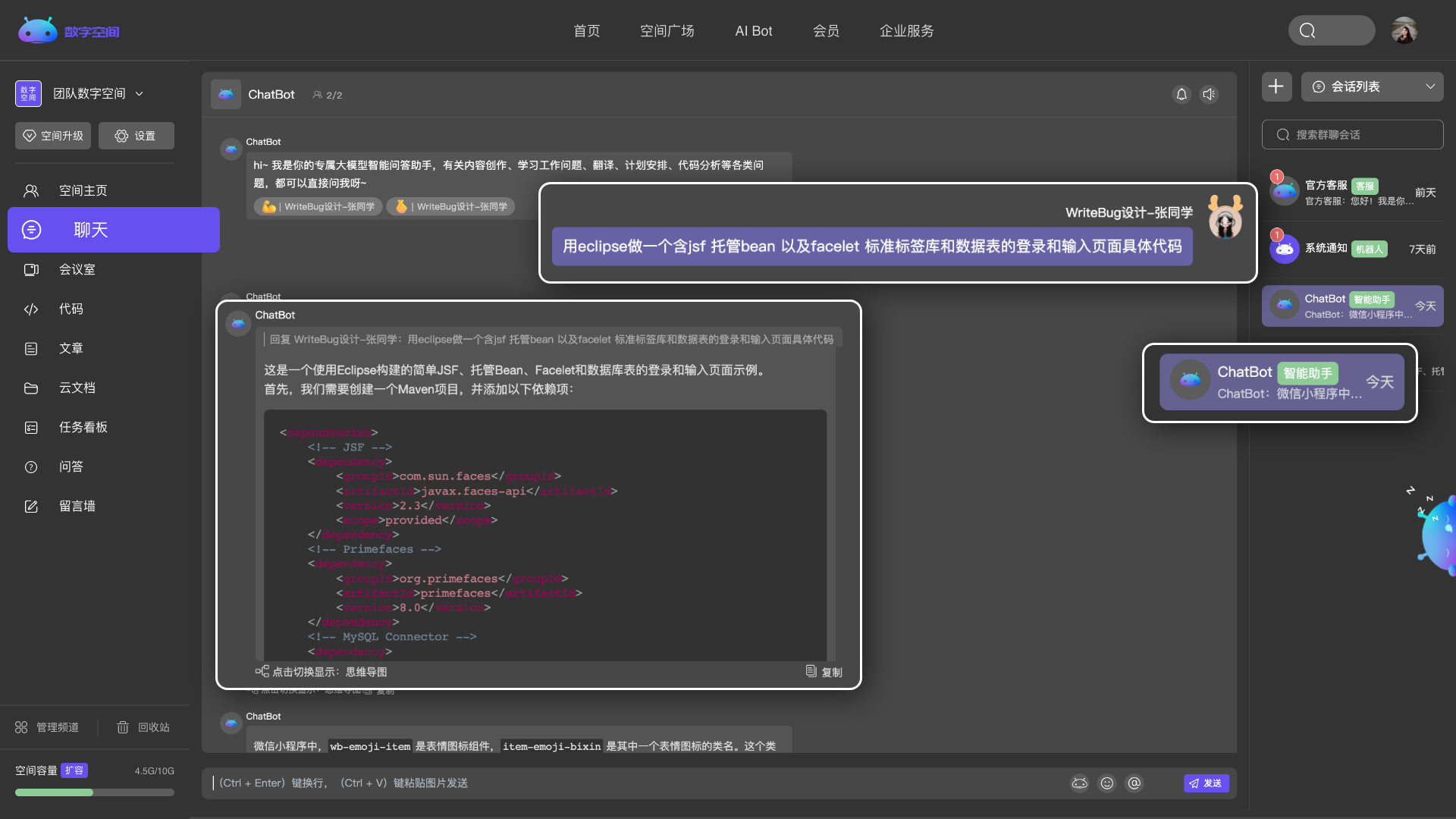
实时查看、共同编辑,更高效的帮你处理学习与工作。















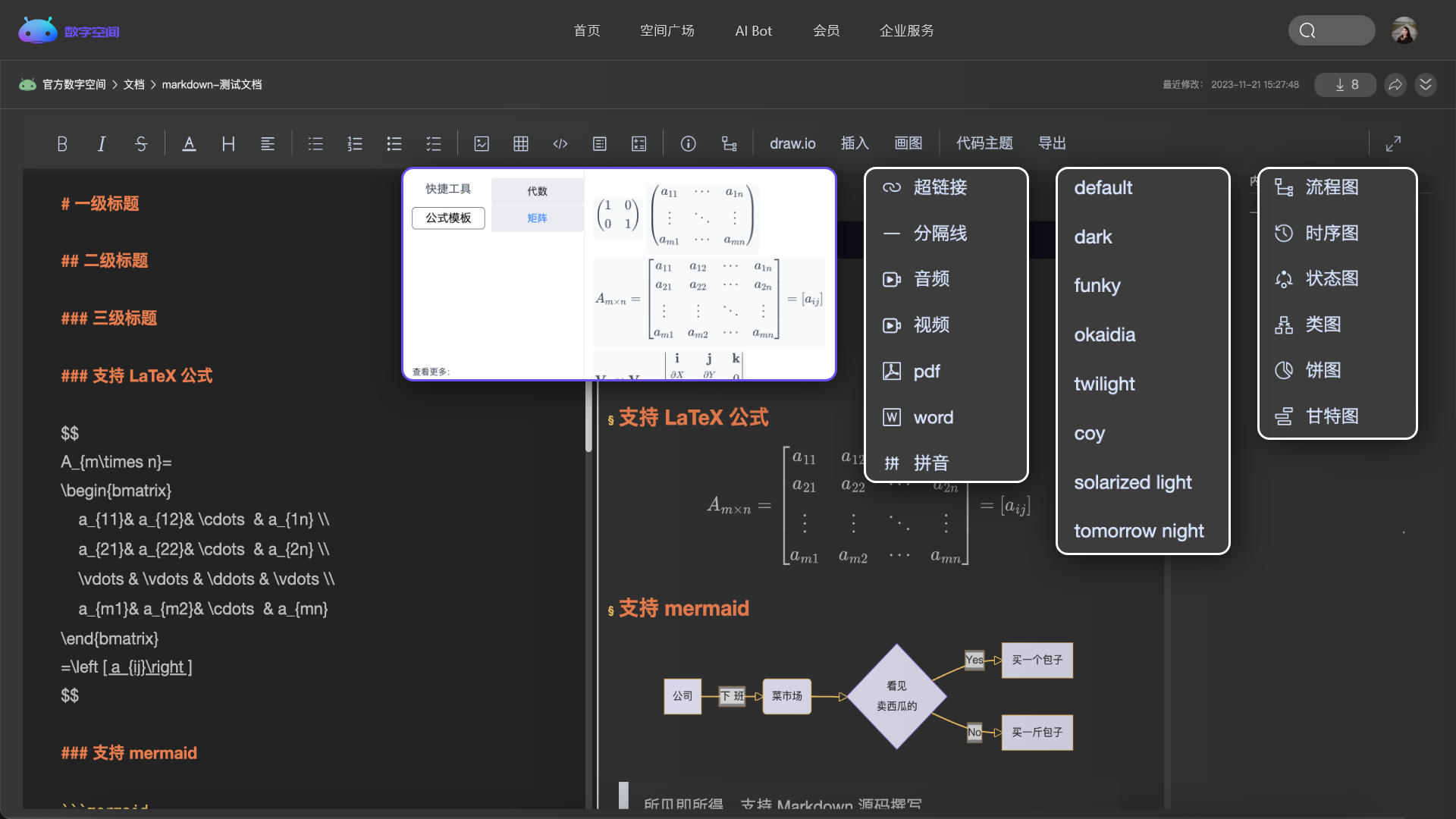
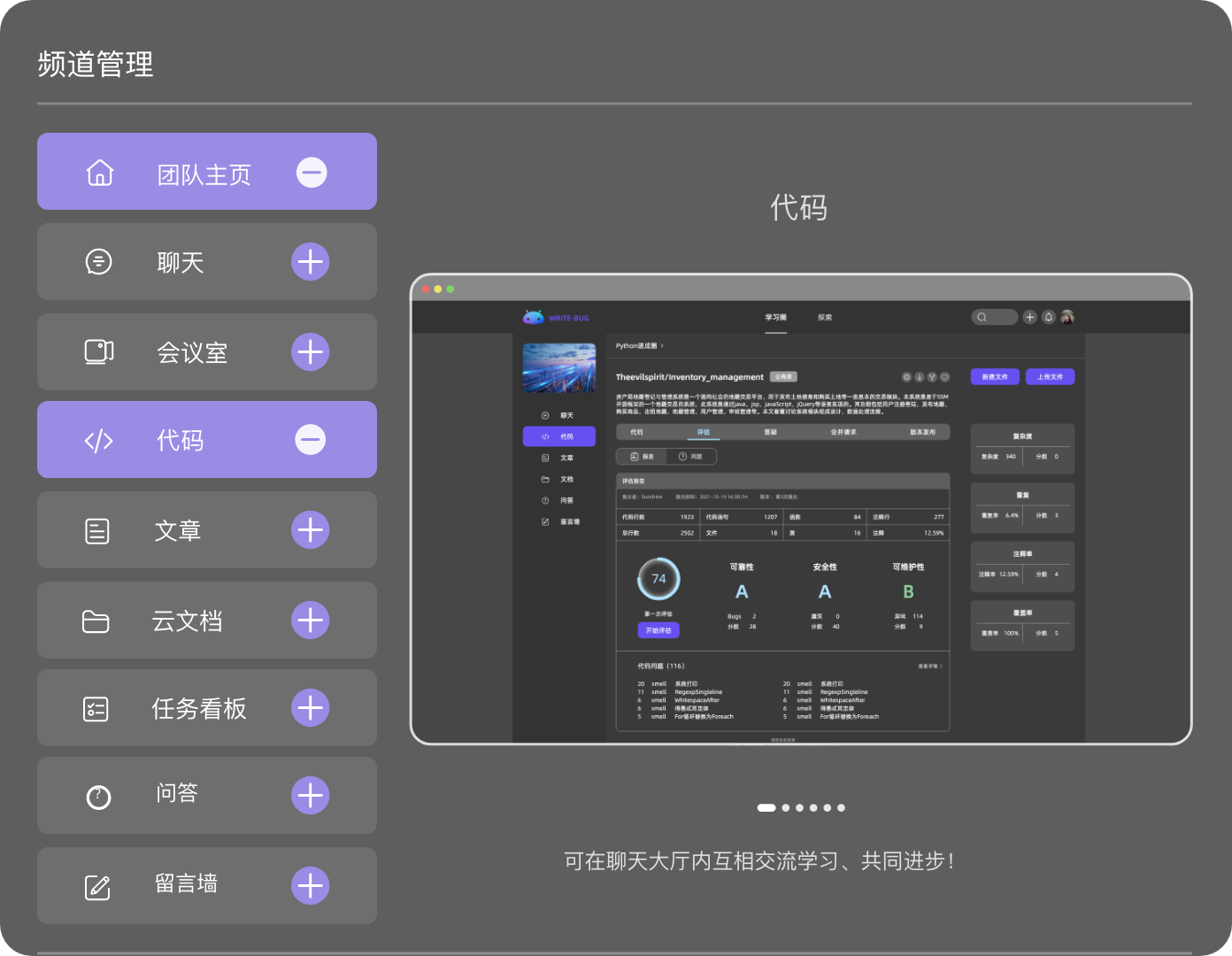
管理你的代码、文章、问答、各类文档和音视频等,所有的内容都在这里。
Explore
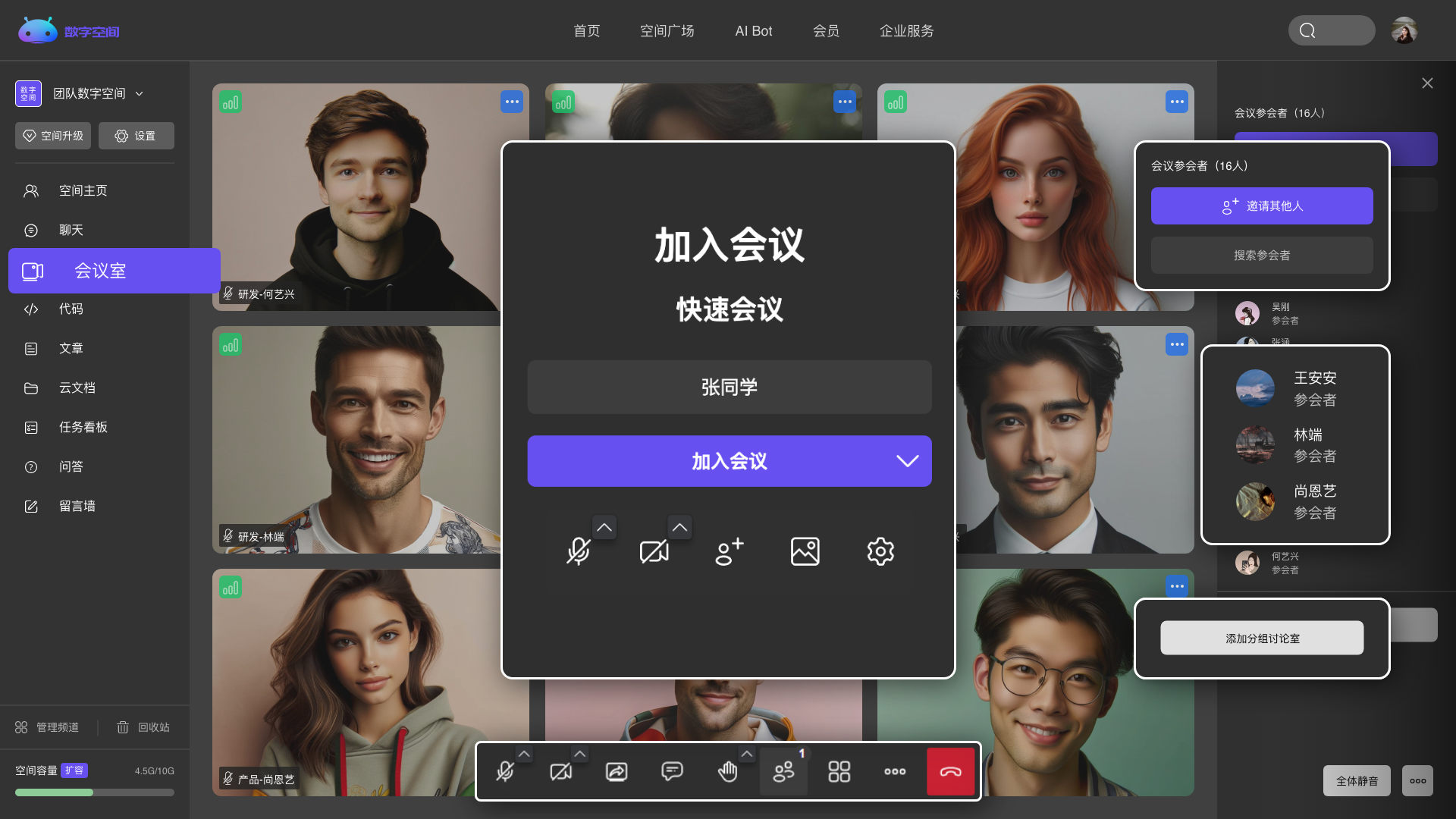
随时发起会议交流,更高效、便捷的进行团队沟通与协作。
Explore
快速识别你的需求,智能回答,帮助你解决学习工作中的任何问题。
Explore
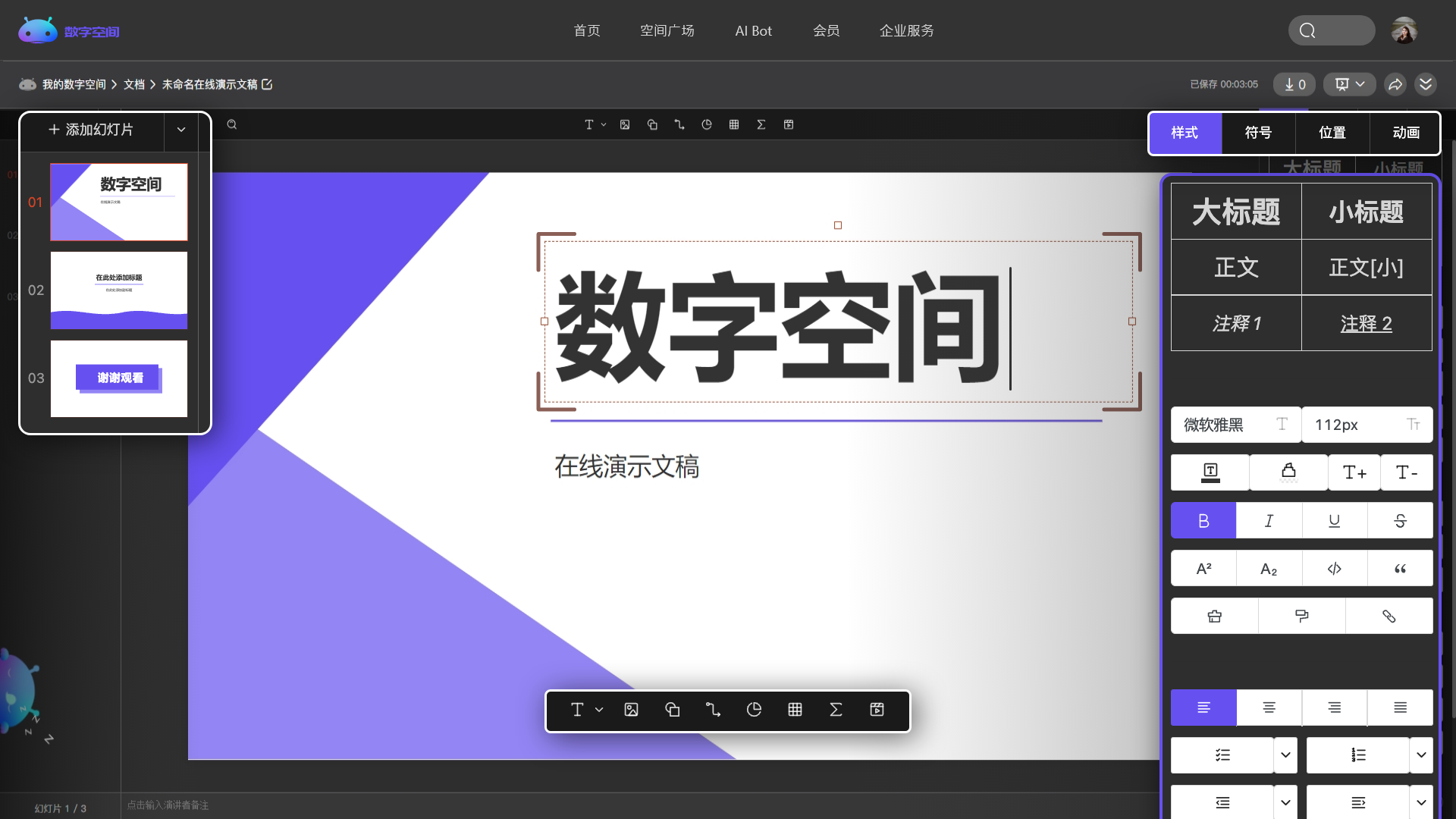
个性展示你的形象、专业技能,做你的专属博客。
Explore
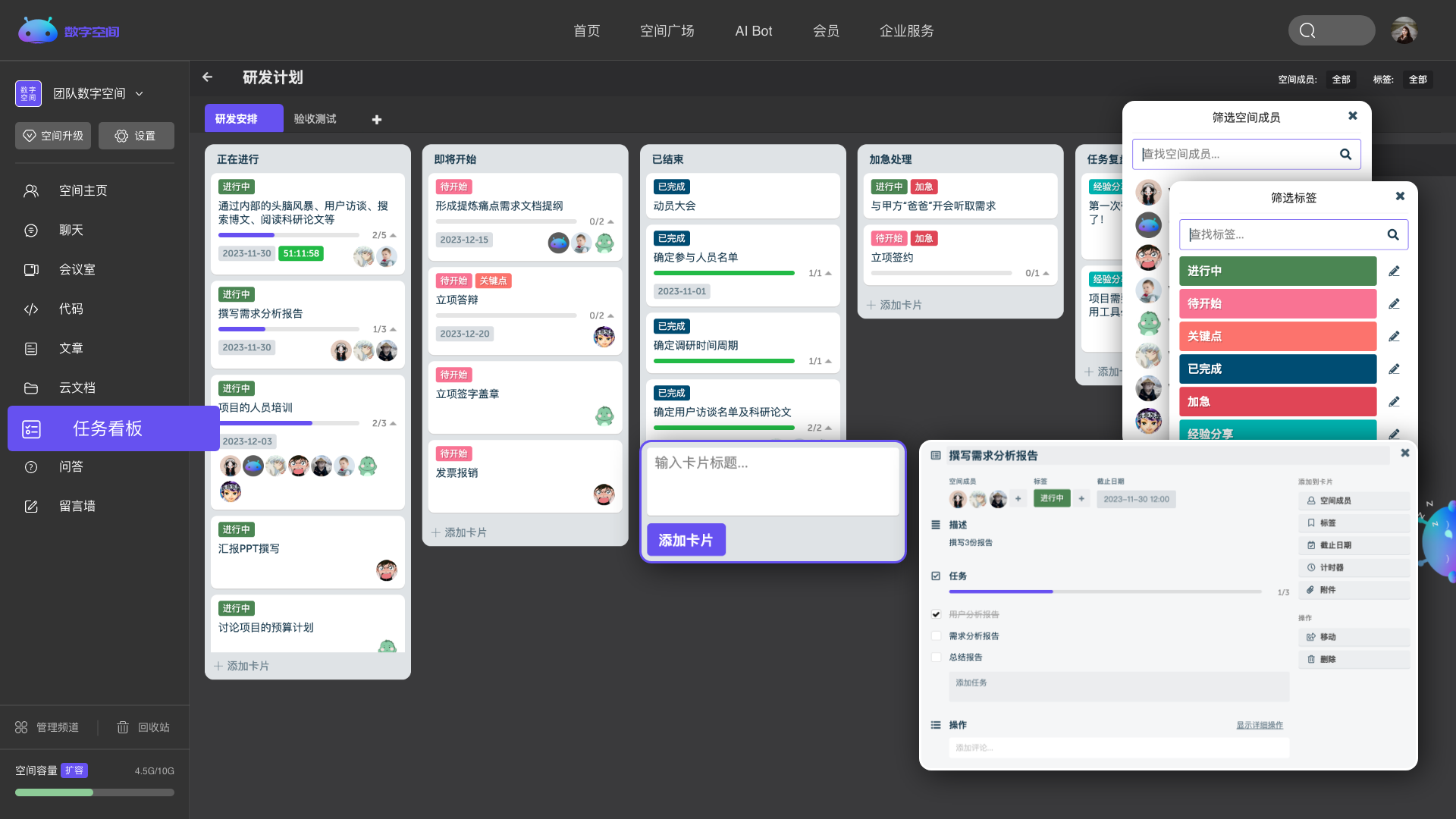
量化工作数据,直观展示任务安排。
Explore


累计注册用户
用户覆盖国内高校
从大一开始就用平台,到现在大四了,功能特别棒,完成了质的飞跃,WRITE-BUG加油!
WRITE-BUG不是指内容输出,更是内容分享、交流,在这里结识有趣的、道合的人,通过平台的赋能,做更多有意义的事,创造更多的价值!!!
希望越来越多的人加入这个平台,大家相互学习,希望WRITE-BUG这个圈子越来越好,不忘初心。